 Building a Quality Culture in Construction: The Value of ISO Standards and Certification
Building a Quality Culture in Construction: The Value of ISO Standards and Certification
In the fast-paced, high-stakes world of construction, integration of quality and safety are paramount. As global construction markets expand, the need for robust quality management frameworks is more critical than ever. International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standards offer a globally recognized set of guidelines and recommendations designed to support organizations in delivering consistently high-quality and safe projects.
While obtaining ISO certification is a significant investment, even organizations that do not pursue formal certification can benefit greatly by following ISO’s guidelines. By fostering a quality culture based on ISO best practices, PMBOK principles, and the USACE Construction Quality Management for Contractors (CQM-C) guidelines, construction companies can enhance operational efficiency, reduce risks, and lay a solid foundation for future certification.
1. Understanding the Importance of ISO Standards in Construction
ISO standards provide a comprehensive framework for improving quality, managing risks, ensuring safety, and supporting sustainability in construction projects. Developed by committees of industry professionals worldwide, ISO standards represent a consensus on the minimum requirements and best practices across various domains, including quality management, environmental impact, health and safety, information security, and more.
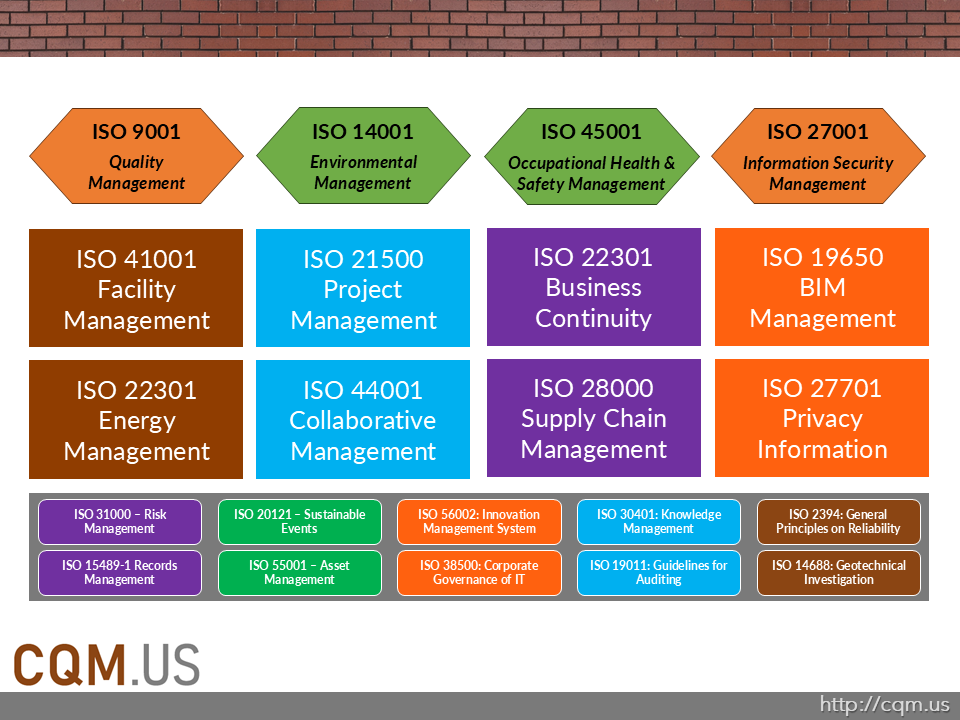
Key standards for the construction industry include:
- ISO 9001 – Quality Management Systems
- ISO 14001 – Environmental Management Systems
- ISO 45001 – Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems
- ISO 27001 – Information Security Management Systems
Each standard is built on the principles of continuous improvement, a risk-based approach, and a focus on customer satisfaction, making them invaluable to construction projects where safety, efficiency, and reliability are essential.
2. Benefits of ISO Certification for Construction Companies
While following ISO guidelines is beneficial, ISO certification brings an added layer of credibility. Certification signals to stakeholders, clients, and regulatory bodies that the organization is committed to maintaining high standards of quality, safety, and sustainability. Here are some key benefits of certification:
-
Enhanced Competitive Advantage: ISO-certified organizations stand out in the marketplace, with certifications often being a prerequisite for bidding on government contracts or partnering with certain clients.
-
Improved Project Quality and Customer Satisfaction: ISO standards focus on meeting client requirements consistently. This focus helps minimize rework, delays, and cost overruns, leading to higher customer satisfaction and project success rates.
-
Risk Management and Safety: ISO standards, such as ISO 45001, emphasize risk assessment and hazard prevention, which are crucial in the high-risk construction environment. By identifying and mitigating risks early, companies can reduce incidents and ensure a safer working environment.
-
Operational Efficiency: Standardizing processes across projects improves communication, minimizes redundancies, and increases efficiency. ISO 9001, for example, outlines methods for efficient resource allocation and continuous process improvements.
3. Following ISO Guidelines Without Certification: Building a Quality-Driven Culture
For organizations not yet ready to pursue ISO certification, aligning with ISO standards can still yield significant benefits. A quality culture based on ISO principles helps establish standardized processes, sets clear expectations, and lays the groundwork for continuous improvement.
3.1. Establishing a Quality Management System (QMS) Aligned with ISO 9001
ISO 9001 focuses on quality management and customer satisfaction, and its framework can serve as a foundational guideline for a quality culture in any organization. By developing a QMS aligned with ISO 9001:
- Define Quality Objectives: Establish specific, measurable quality goals that align with project requirements and client expectations.
- Document Processes: Clearly define and document key processes, including roles and responsibilities, workflows, and checklists.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and refine processes based on feedback and performance data, focusing on root-cause analysis and corrective actions.
Implementing these practices helps ensure project consistency and facilitates a transition toward ISO certification if the organization chooses to pursue it later.
3.2. Fostering Safety and Environmental Responsibility
Standards such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) provide guidelines for integrating sustainability and safety into construction practices. Even without certification, construction companies can:
- Conduct Environmental Impact Assessments: Evaluate the environmental impacts of projects and take steps to reduce waste, pollution, and resource consumption.
- Implement Health and Safety Protocols: Create a safe work environment by identifying potential hazards, training employees, and enforcing safety measures aligned with ISO 45001 standards.
- Engage in Continuous Safety Training: Ensure ongoing safety training for employees to promote awareness, proper equipment handling, and emergency preparedness.
These practices can reduce legal liabilities, promote a safe work environment, and improve the company’s reputation among clients and regulatory agencies.
3.3. Ensuring Information Security
Data security is increasingly critical in construction, with sensitive data (such as design blueprints, financial records, and project details) at risk of unauthorized access. ISO 27001 provides a framework for protecting information assets:
- Access Control and Data Management: Implement strict access controls to ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data.
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Regularly assess data security risks and vulnerabilities, implementing measures to mitigate potential breaches.
- Employee Training on Data Security: Educate staff about data security protocols, including the importance of secure passwords and responsible data handling.
By following these guidelines, companies can minimize risks and safeguard client and project information.
4. Integrating Best Practices from PMBOK and USACE CQM-C
While ISO standards provide a global framework, combining ISO principles with best practices from the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) and USACE’s Construction Quality Management for Contractors (CQM-C) can further strengthen a quality-oriented culture.
4.1. PMBOK: A Framework for Effective Project Management
The PMBOK framework offers a structured approach to managing construction projects through its ten knowledge areas, including quality, risk, and stakeholder management. Implementing PMBOK principles enables teams to:
- Enhance Project Planning and Control: PMBOK’s emphasis on detailed planning and risk assessment complements ISO’s risk management approach.
- Improve Communication: PMBOK stresses the importance of clear, consistent communication with stakeholders, which aligns with ISO’s focus on stakeholder engagement.
- Support Quality Assurance and Quality Control: PMBOK’s quality management processes provide practical methods for ensuring project deliverables meet specifications.
4.2. USACE CQM-C: Ensuring Quality in the Construction Environment
The USACE Construction Quality Management for Contractors (CQM-C) program is widely recognized as an industry best practice. Key takeaways from the program that align with ISO principles include:
- Three-Phase Control System: The USACE CQM-C emphasizes pre-construction planning, ongoing inspections, and final inspections to ensure quality compliance at every stage.
- Continuous Quality Checks: Routine inspections and prompt issue resolution, as prescribed by CQM-C, align well with ISO’s continuous improvement philosophy.
- Documentation and Reporting: CQM-C’s focus on documentation provides valuable insights for tracking quality performance, which supports the ISO requirement for maintaining records of compliance.
5. Steps for Preparing for Future ISO Certification
If ISO certification is a long-term goal, organizations can take proactive steps to prepare for certification while adopting a quality-driven culture.
-
Conduct a Gap Analysis: Identify gaps between current practices and ISO standards. Understanding these gaps allows organizations to prioritize improvements effectively.
-
Implement Internal Audits: Regular internal audits help ensure compliance with established processes and highlight areas for improvement. These audits mimic the ISO certification process and prepare teams for formal certification audits.
-
Develop an Integrated Management System (IMS): An IMS, as recommended in the Annex SL framework, allows organizations to combine quality, environmental, health, safety, and information security management into a unified system, streamlining processes and simplifying future ISO certification efforts.
-
Train and Empower Employees: Provide training to employees on ISO principles, quality control techniques, and safety practices. By empowering employees with knowledge and resources, companies can build a workforce committed to maintaining high standards.
-
Engage Leadership: Leadership commitment is essential in fostering a quality culture. Leaders should champion quality initiatives, allocate resources, and communicate the value of ISO-aligned practices.
Minimum
-
ISO 9001 – Quality Management Systems
Focuses on improving quality and customer satisfaction through structured quality management processes. Essential for streamlining construction processes and reducing errors. -
ISO 14001 – Environmental Management Systems
Supports sustainable construction practices by reducing environmental impact, waste, and compliance risks. Vital for companies committed to eco-friendly operations. -
ISO 45001 – Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems
Reduces workplace accidents and improves health and safety performance by identifying and mitigating hazards. Critical in high-risk construction environments. -
ISO 27001 – Information Security Management Systems
Ensures data protection, especially sensitive information like project plans, financial records, and employee data. Important for securing construction company data.
Recommended
-
ISO 50001 – Energy Management Systems
Helps organizations improve energy efficiency, reduce costs, and align with global energy regulations. Essential for sustainable operations in large facilities like SLAC. -
ISO 22301 – Business Continuity Management Systems
Prepares companies to withstand disruptions (natural disasters, supply chain issues), enhancing resilience and ensuring project continuity. -
ISO 41001 – Facility Management – Management Systems
Provides a framework for effective facility operations, addressing areas such as maintenance, resource efficiency, and asset lifecycle management. -
ISO 21500 – Project Management – Guidance on Project Management
Outlines best practices for planning, managing, and delivering construction projects, ensuring alignment with strategic objectives and efficient resource allocation. -
ISO 28000 – Supply Chain Security Management Systems
Secures supply chains by enhancing reliability and managing risks in procurement processes, crucial for large, complex construction projects. -
ISO 27701 – Privacy Information Management System (PIMS)
An extension of ISO 27001 that aligns with GDPR and other privacy laws, helping organizations manage and protect personal data effectively. -
ISO 19650 Series – Information Management using BIM (Building Information Modeling)
Supports construction and facility management by standardizing data management practices through BIM, improving coordination and reducing project errors. -
ISO 44001 – Collaborative Business Relationship Management
Facilitates collaboration with stakeholders (contractors, engineers, suppliers) by setting a framework for partnerships, enhancing project success through cooperation.
These standards collectively support construction companies in achieving regulatory compliance, enhancing operational efficiency, ensuring safety, and promoting sustainable practices.
Conclusion: Building a Culture of Quality for Long-Term Success
ISO standards offer valuable guidelines for the construction industry to enhance project quality, safety, and environmental stewardship. While ISO certification adds credibility, the journey to adopting ISO-based best practices is a powerful step in itself. By embracing a quality culture grounded in ISO principles, PMBOK standards, and USACE CQM-C practices, construction companies can improve operational efficiency, mitigate risks, and set the stage for future growth.
The construction industry is becoming increasingly competitive, and quality is a key differentiator. Adopting ISO-aligned best practices demonstrates a commitment to excellence, positioning companies as trustworthy partners in a demanding market. For construction organizations ready to stand out, ISO standards offer a pathway to achieving world-class quality and safety in every project.
References
- International Organization for Standardization. (n.d.). “ISO – Standards.” www.iso.org
- Project Management Institute. (2017). PMBOK® Guide – Sixth Edition.
- U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. (n.d.). Construction Quality Management for Contractors (CQM-C).
- ISMS.online. (n.d.). “ISO for the Construction Industry.” www.isms.online
Disclaimer: This whitepaper provides general information and does not constitute professional advice.