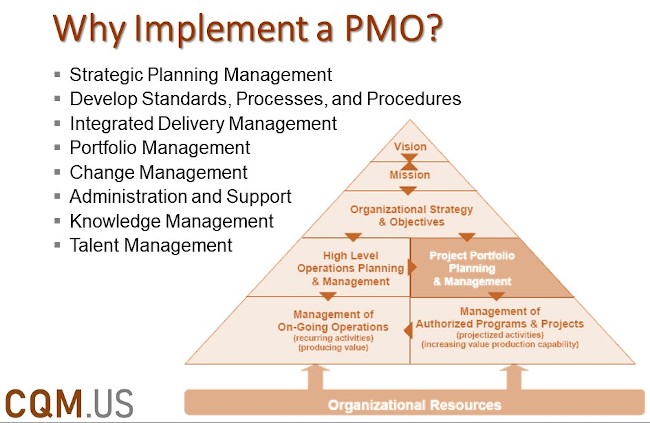
Establishing a Project Management Office or PMO for CQM is an essential initiative by the organization to standardize processes, align strategies, set expectations, collect lessons learned, and transfer knowledge into BI4CQM. The PMO for CQM is also called the center of excellence or center of expertise. The CQM Methodology will not cover the process to establish a PMO in an organization, however, CQM Experts are Project Management Professionals that have either established PMO or worked in a PMO before and could be a great resource to assist in establishing a PMO for CQM in construction-related organizations and companies.
Reading this section will help managers realize the benfits of establishing a PMO to drive the following values and benefits:
- Proper identification of scope requirements and eliminating scope creep by due diligence review of the contract document,
- managing stakeholders and compliance with regulatory entities through clear and concise communication,
- promoting safety-first mentality and quality excellence culture awareness through preventive approach supervision,
- qualitative risk analysis and elimination of errors by effective change management and early claim management,
- project control of schedule and budget using Earned Value Management to increase productivity and improve efficiency,
- upholding professional and ethical conduct coupled with high emotional quotient and interpersonal skills,
- advance supply chain management with prequalification assessment for procurement management,
- continuous learning and improvement by use of innovative technologies to increase productivity and automation,
- sharing knowledge and best practices by collecting lessons learned through accessible knowledge database, and
- improve the organization’s profitability while considering sustainability goals and social responsibilities.
What is a PMO?
PMO or Project Management Office was first introduced by Project Management Institute as a central office for Project Managers of an organization to gather and share knowledge, collaborate on practices, and standardize processes to streamline the continuous quality improvement process related to Project Management per PMBOK framework. Later, Program and Portfolio Management Offices were introduced to do the same at Program and Enterprise level of the organizations, with managers from different disciplines such as Business, IT, Engineering, Marketing, Legal, and Operation gathering in a central office to develop standards, processes, and governance needed to align organizations’ strategic goals with the program and portfolio management. Therefore, when referring to PMO one must define whether it is for Project, Program and Portfolio. All PMO have common goals and similar processes, but with different domains and jurisdictions defining their governance.
What are the benefits of a PMO?
In project-driven organizations such as the ones in the Construction Industry, the ad hoc approach to PM is the traditional norm where each project manager has developed his style of management, based on his acquired knowledge, education, and past project experience. The traditional approach to PM leads to inefficiencies and can even be dangerous, while the establishment of a PMO can foster consistency and nurture PM Professionalism. (Xiaoyi Dai)
There are many benefits of establishing a PMO to standardize and enforce governance in an organization, here is a shortlist of benefits of a PMO (Dr. Hobbs):
- Participate in strategic planning
- Report project status to upper management
- Provide advice to upper management
- Develop and implement a standard methodology
- Monitor and control project performance
- Develop competency of PM personnel, including training
- Provide mentoring for project managers
- Implement and operate a project information system
- Coordinate between projects
- Develop and maintain a project scoreboard
- Promote project management professionalism within organization
- Identify, select and prioritize new projects
- Manage archives of project documentation
- Provide a set of tools in an effort to standardize
- Execute specialized tasks for project managers
- Allocate resources between projects
- Conduct project quality audits and post-project reviews
- Implement and manage a database of lessons learned
- Implement and manage a risk database
- Manage Business Intelligence for Benefits and Value
- Conduct networking and environmental scanning
- Recruit, select, evaluate and determine salaries for project managers
- Manage customer interfaces and satisfaction (internal and external)
PMO for CQM
All of the mentioned PMO benefits are focused on improving the project management quality and promoting a Quality Excellence Culture within the organization. However, to summarize the PMO4CQM mindset on how PMO for CQM Methodology and Framework will benefit construction companies here is the main points:
- Centralize Quality Assurance and Project Audits
- Increases focus on ‘doing the right things’
- Increases quality of ‘doing things right’
- Reviews Project artifacts objectively
In the traditional Construction Quality Management in Construction Projects, CQM Managers are usually seen as the policing force to whistleblow deficiencies and lack of workmanship and quality. However, establishing a PMO for CQM will take that burden and negative mindset away, where PMO is seen as the governing body and CQM Managers are the liaison between the organization’s expectation and Project Manager’s performance. Therefore, depending on the maturity and size of the organization the types of PMO could be in either of the following levels:
- Supportive
- Consultant to projects providing best practices, templates, training, lessons learned, etc.
- Very low control/influence over projects
- Works where projects can succeed in a loosely controlled manner
- Controlling
- Requires compliance with their frameworks/methodologies
- Might require regular reviews
- Works if compliance will bring improvements and if PMO has sufficient executive support
- Directive
- Directly manages projects; high degree of control/influence
- Injects professionalism in project
- Effective in a larger matrix or hierarchical organizations
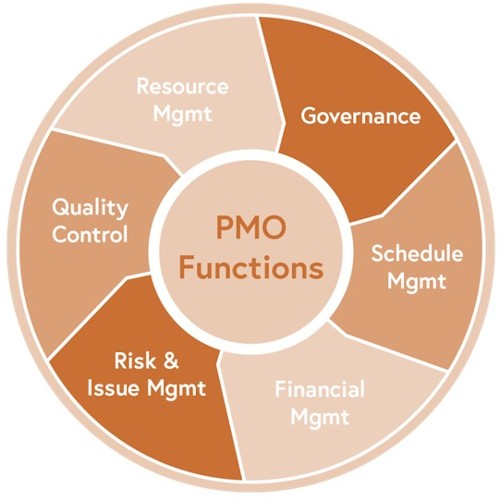
Establishing a PMO4CQM
This brief section will not be sufficient to discuss all of the aspects and benefits of a PMO for CQM, however, in different parts of the CQM Methodology, references are made to the need of a PMO, and this section was presented to introduce the concept of PMO4CQM. Further detailed information and discussion will be presented in a half-day workshop or a short version lunch+learn as part of the CQM Training. However, to introduce some of that discussion, the Deploying steps of a PMO are introduced as follows:
- Promote Culture change
- Evaluate aspects of driving behavior
- Reinforce Positive and eliminate negative attitudes
- Promote Enablers and shift paradigms for Quality Excellence Culture Mindset
- Deploy PMO in waves
- Get Top Management Buy-in
- Don’t change things all at once
- Support/Control/Direct phases
- Create (or buy) a project methodology
- Processes and Procedures
- Templates, Standards, Guidelines, and Policies
- Best Practices and Methodology Management
- Provide training and coaching
- Development & Training
- Support & Coaching
- Enhancements
- Conduct audits/assessments
- Project-level audits: risks, deliverables, project controls, etc.
- Organizational-level audits: Gap analysis and PMO effectiveness
- Consider the learning curve and have patience
- Provide consolidated metrics
- Clear and Concise
- Use of Standards and Automated
- Consolidate metrics and reportings
- Consulting firms can fill gaps
- Benchmarking
- Best Practices
- Interpersonal Skills
Promoting the PMO
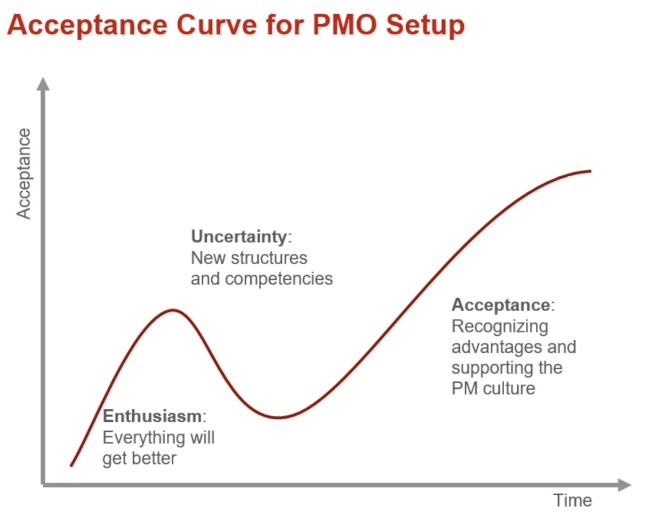
There will be many resistance from the Project Management Team and other lower tiers to comply with a standardized process and procedure dictated and directed by PMO. Therefore obtaining buy-in and increasing PMO Acceptance within the Organization is an up-down-up cycle of enthusiasm in the beginning, uncertainty, and dip, and back to rise after acceptance and recognizing the advantages of a PMO. Therefore Interpersonal Skills and proper communication with professional Stakeholder management are essential to the success of a PMO.
A team of managers organizing the PMO and promoting it have the responsibility to “Close the Loop!” This means that they have to inform the organization and all relevant stakeholders of the true result and status of PMO effectiveness by transparency, increased dependability, and signifying a commitment to go through all the challenges to promote and establish the PMO culture.
PMO Success Factors are:
- Backing from management
- Organizational position
- Areas of responsibility and competencies
- PMO employee qualifications
- Presenting quick successes
- Recording progress
- Transparency within the company
- Appropriate communication
- Building trust
- Taking one small step at a time